Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The Carpal Tunnel is a passage in the wrist, where the median nerves pass through this tunnel to connect the hand and forearm. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is used to describe the compression or pinching of the median nerve as it passes through the wrist joint, causing numbness and pain in the wrist, palm, and fingers.
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is most commonly triggered by repetitive motions such as typing or sports. Some of the risk factors of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome are as follows:
- High-force and extreme wrist motions
- Hand or wrist deformity
- Pregnancy
- Haemodialysis
- Heredity (smaller carpal tunnel can run in families)
- Health conditions (Diabetes, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and thyroid imbalance)
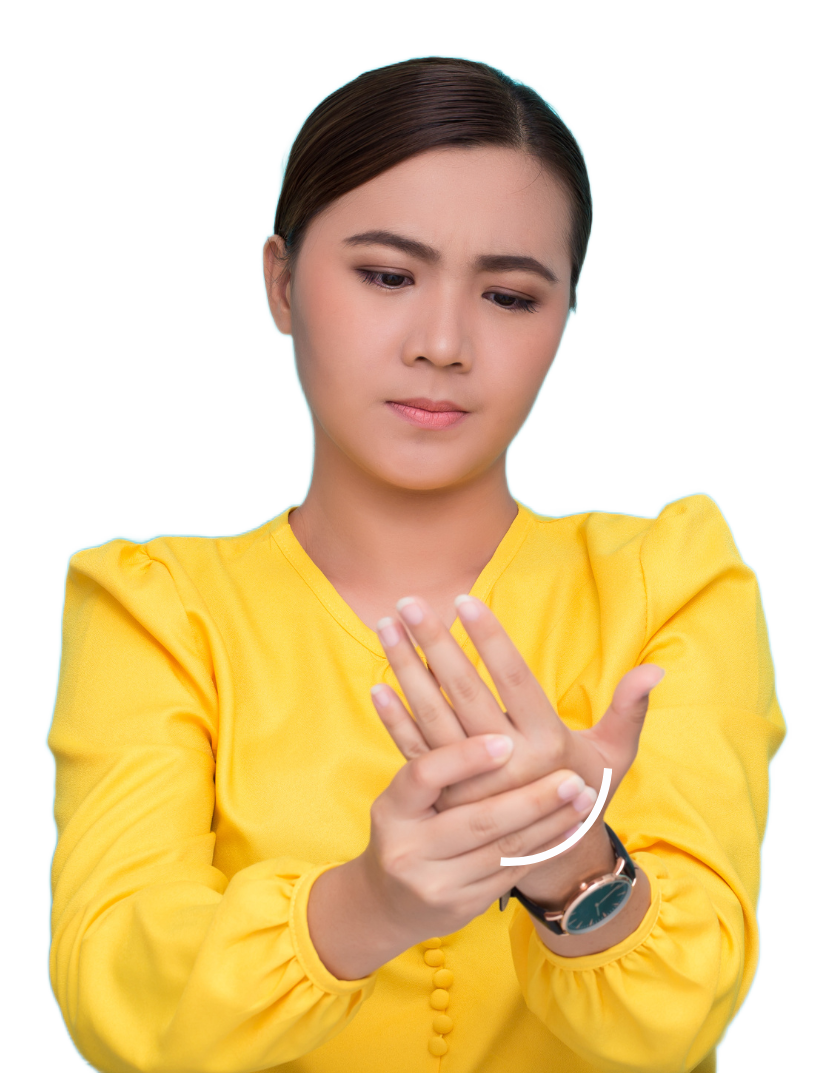

Symptoms Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Pain
Weakness
Other symptoms
A Message About Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The pain and numbness of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome often mimic symptoms of nerve compression. Together with pain and stiffness in the neck and shoulder, the pins and needles in the hands may cause the patient to worry about cervical spinal nerve compression. The feeling of “poor blood flow” in the hand may cause weakness, resulting in difficulty opening jugs or containers. The fine motor skills of the fingers may be affected, causing difficulties in buttoning or picking up things with fingers.
Depending on the severity of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, significant narrowing of the tunnel may have to be surgically decompressed. Mild to moderate narrowing usually may be treated adequately with less invasive injections.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Our team of experienced primary care physicians or pain care specialists together with a hand surgeon will conduct a thorough diagnosis. This includes a physical exam, questions about your symptoms, and an evaluation of your medical history. Additional tests may be conducted such as the Tinel sign test where the physician taps over the median nerve at the wrist and see if it produces a tingling sensation in the fingers. An X-ray may be needed if the wrist is limited in motion or there is evidence of arthritis or trauma.
What Treatments Are Available for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that worsens over time, early diagnosis and treatment can make the treatment easier and more effective. At Singapore Paincare, we strive to treat your pain with the least invasive option possible after accurately identifying the cause. Our approach to pain resolution focuses on the removal of pain generators via specialised injection and minimally invasive procedures. Combined with pharmacological treatments and cognitive and physical rehabilitative therapies – we help patients improve functions and prevent pain from recurring.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Splinting
Coreflex Steroid Injections
In general, if one should need repeated injections (more than 2 times), further evaluations with MRI investigations may be warranted by our specialists before more injections are administered to the painful area.
Physiotherapy
Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Surgical Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome generally responds well to conservative treatments. If the problem does not respond to non-invasive treatments or if it becomes severe, surgery may be an option. As surgery always comes with associated risks, complications, and downtime – it may not be suitable for everyone. You should carefully weigh the decision before deciding to go under the knife by considering the pros and cons of both non-surgical methods and surgical reconstruction.
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
How Can I Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome can be difficult since the condition is caused by so many activities in a person’s daily life. Here are a couple of methods that can help minimise some factors that can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Keeping your wrists straight when using tools
- Avoid curling, flexing or extending your wrists repeatedly
- Ensure proper seating, hand and wrist placement when using computers
- Take frequent breaks when doing repetitive activities
Get Your Pain Resolved
Send your enquiries or consult our pain experts today.