Recognising Cardiac-Related Shoulder Pain
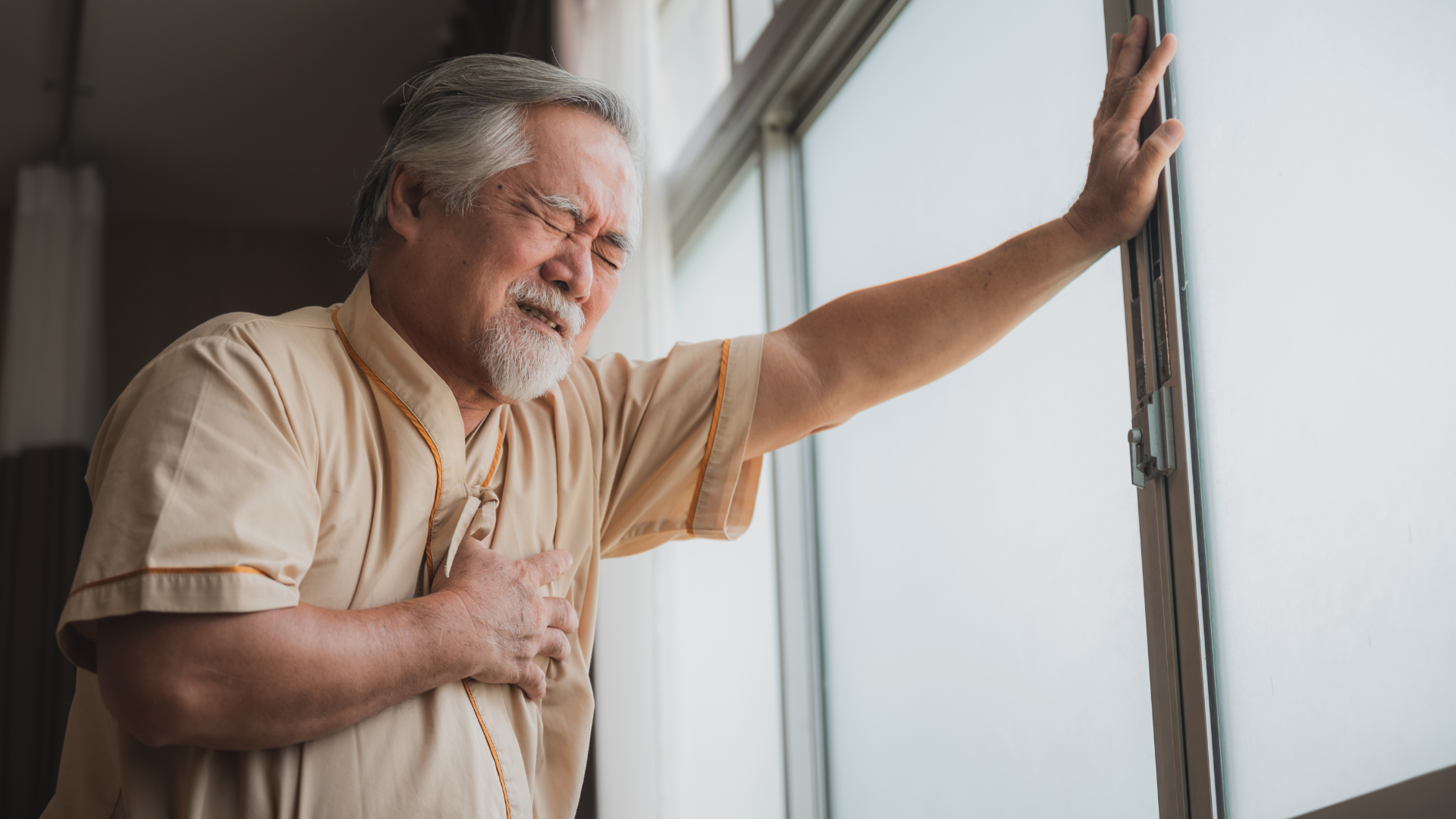
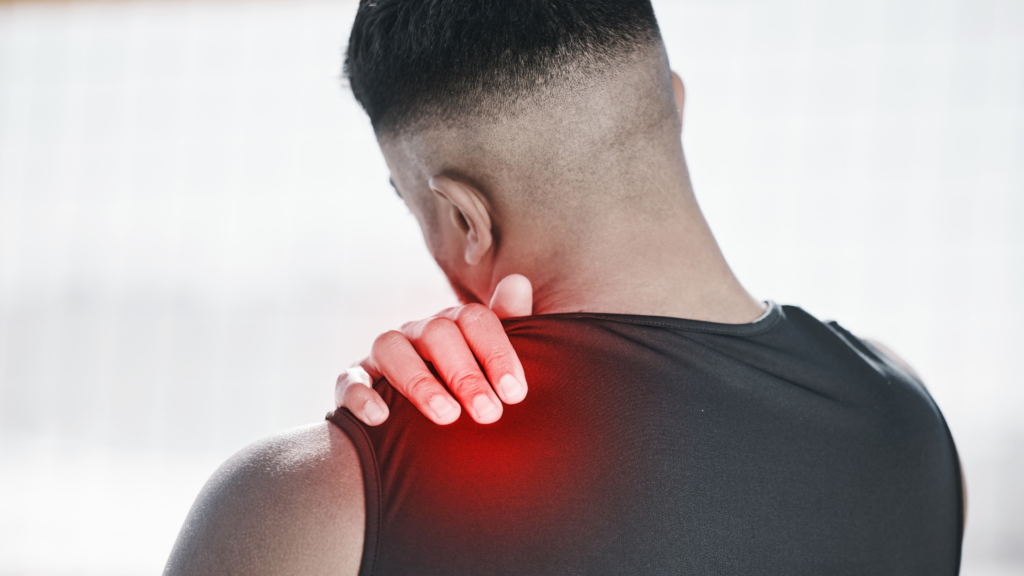
Identifying cardiac-related shoulder pain is a critical aspect of potentially life-saving early intervention. Shoulder pain can vary in its presentation, and not all instances are indicative of a heart attack. However, there are distinct characteristics, associated symptoms, and risk factors that can serve as valuable indicators when assessing whether shoulder pain might be connected to a cardiac event.
Characteristics
When evaluating shoulder pain as a potential symptom of a heart attack, understanding its specific characteristics is essential. Cardiac-related shoulder pain may exhibit the following traits:
- Radiating Pain: One hallmark of shoulder pain associated with a heart attack is its propensity to radiate from the chest into the left shoulder or occasionally the right shoulder. This radiating pain is often described as a heavy or squeezing sensation, distinct from the sharp or localized discomfort typical of musculoskeletal issues.
- Persistent Pain: Unlike ordinary muscle soreness or minor discomfort that might ease with rest or posture adjustments, heart-related shoulder pain tends to be persistent. It doesn’t subside easily, even when you alter your position or activity level.
- Exacerbation with Activity: Cardiac-related shoulder pain may intensify with physical activity or heightened stress levels. This escalation in pain, especially when accompanied by other cardiac symptoms like chest pain, is a concerning sign that should not be disregarded.
- Left vs. Right Shoulder Pain: While cardiac-related shoulder pain is often associated with the left shoulder, it’s important to note that it can also affect the right shoulder, particularly in certain cases. The presence of similar characteristics in right shoulder pain should be evaluated with the same degree of caution.
Warning Signs That It Might Be A Heart Attack
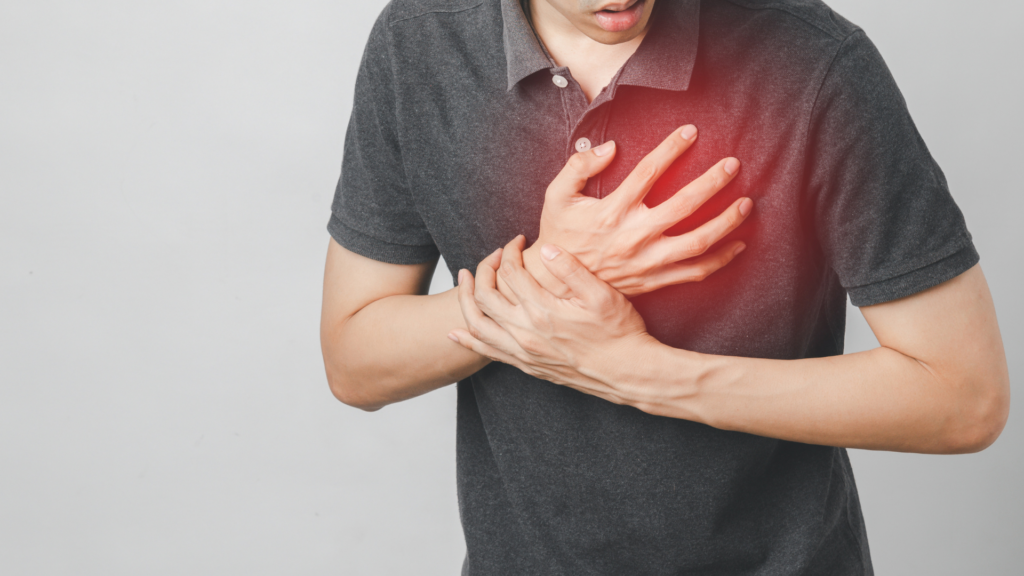
Shoulder pain, as a potential indicator of a heart attack, seldom exists in isolation. It is frequently accompanied by other warning signs that demand attention. These associated symptoms include:
- Chest Pain: Perhaps the most widely recognized symptom of a heart attack, chest pain or discomfort is usually felt behind the breastbone or on the left side of the chest. It is often described as a crushing or burning sensation.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, particularly when it occurs suddenly or in conjunction with shoulder pain, should be a cause for concern. It can manifest as rapid, shallow breathing or a feeling of breathlessness.
- Nausea and Sweating: The presence of nausea, vomiting, or profuse sweating can be associated with cardiac-related shoulder pain. These symptoms often accompany chest pain and shortness of breath during a heart attack.
Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors that can heighten the likelihood of experiencing cardiac-related shoulder pain is vital for early recognition and prompt medical intervention. These risk factors include:
- Age and Gender: Men over the age of 45 and women over the age of 55 are at a higher risk of heart attacks. However, it’s crucial to note that heart attacks can occur in younger individuals as well.
- Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease and heart attacks. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Hypertension is a significant risk factor for heart attacks. Elevated blood pressure can strain the heart and damage the arteries, increasing the chances of coronary artery disease.
- High Cholesterol (Hypercholesterolemia): Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) can contribute to the development of coronary artery disease, which is a leading cause of heart attacks.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease can predispose individuals to a higher risk of heart attacks. Genetics can play a role in the development of cardiovascular conditions.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can increase the risk of heart problems. Elevated blood sugar levels can harm blood vessels and the heart itself.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can strain the heart and increase the likelihood of heart attacks. Excess body fat can contribute to conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
Recognising these risk factors is crucial for understanding when shoulder pain may be related to a heart attack. If you or someone you know experiences shoulder pain with any of these characteristics, associated symptoms, or risk factors, seeking immediate medical attention is paramount.
Other Possible Reasons for Shoulder Pain
While cardiac-related shoulder pain is a serious and potentially life-threatening concern, it’s essential to recognise that various other conditions and factors can lead to shoulder discomfort. A comprehensive evaluation is crucial to accurately diagnose the source of shoulder pain and determine the most appropriate treatment. Let’s explore some of the other potential reasons for shoulder pain.
Muscle and Soft Tissue Issues
Muscle and soft tissue problems are among the common culprits for shoulder pain. These issues encompass a range of conditions that affect the muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues in the shoulder area:
Muscle Strain
A muscle strain occurs when the shoulder muscles are subjected to excessive force, often due to overexertion, lifting heavy objects, or sudden, uncontrolled movements. The result is pain in the shoulder region, which can range from mild discomfort to more severe pain. Rest, ice, and gentle stretches can help alleviate muscle strain-related shoulder pain.
Rotator Cuff Injury
The rotator cuff comprises a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Injuries to the rotator cuff can lead to significant shoulder pain, especially during specific movements like reaching overhead or lifting objects. Rotator cuff injuries may range from mild inflammation (tendinitis) to tears that require medical intervention, such as physical therapy or surgery.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis refers to the inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder. It can result from repetitive movements or overuse of the shoulder joint, leading to pain, swelling, and restricted mobility. Treatment for tendinitis often includes rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Bursitis
Bursitis occurs when the bursa sacs, which cushion the shoulder joint and reduce friction, become inflamed. This inflammation can cause discomfort and restricted motion in the shoulder. Treatment for bursitis typically involves rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and, in some cases, physical therapy to restore shoulder function.
Joint and Bone-Related Causes
Shoulder pain can also originate from joint and bone-related issues, affecting the stability and function of the shoulder:
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. It typically progresses through stages, starting with pain and ending with a gradual improvement in mobility. Physical therapy and exercises play a crucial role in the management of a frozen shoulder, helping to regain range of motion.
Arthritis (Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis)
Arthritis, whether osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, can lead to chronic shoulder pain due to joint inflammation and damage. Management strategies for arthritis-related shoulder pain may include medications to reduce inflammation, physical therapy to improve joint function and lifestyle modifications.
Fracture
A fracture or broken bone in the shoulder area can result in severe pain. This type of shoulder pain often requires immediate medical attention to assess the extent of the injury and may involve immobilization, casting, or surgery, depending on the severity of the fracture.
Nerve-Related and Referred Pain
Nerve-related and referred pain can sometimes be the underlying cause of shoulder discomfort:
Nerve Compression (Brachial Plexus)
Compression or injury to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that control the shoulder, arm, and hand, can lead to pain in the shoulder. Conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome or nerve entrapment may result in brachial plexus compression and require specialised evaluation and treatment.
Internal Health Issues
Certain internal health issues can manifest as shoulder pain, even though the source of discomfort is located elsewhere in the body:
Gallbladder Disease (Referred Pain)
Gallbladder problems, such as gallstones or inflammation, can cause pain that radiates to the right shoulder. This type of referred pain may be accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain and digestive issues.
Lung Conditions (Referred Pain)
Lung conditions like pneumonia or lung cancer can lead to referred pain in the shoulder area. This occurs when the pain signals from the lungs are perceived in the shoulder. Respiratory symptoms often accompany such shoulder pain.
Digestive Issues (Referred Pain)
Digestive problems, including inflammation of the diaphragm, can cause shoulder pain that originates from the abdominal area. It’s essential to consider the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms when evaluating this type of referred pain.
Understanding the various potential causes of shoulder pain is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you experience persistent or severe shoulder pain, particularly when accompanied by concerning symptoms, consulting a doctor for a comprehensive evaluation is crucial. Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective management and relief from shoulder discomfort.
What to Do If Your Shoulder Hurts
When you find yourself grappling with shoulder pain, it’s essential to take the right steps for relief, recovery, and appropriate management. Shoulder pain can be caused by various factors, including muscle strain, injuries, or underlying medical conditions. Here’s a detailed look at what you can do when your shoulder hurts:
Rest
If you suspect that your shoulder pain is a result of muscle strain, overuse, or an acute injury, one of the initial and most crucial steps is to allow your shoulder to rest. Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain, and give your shoulder the time it needs to heal. Adequate rest is often the first line of defense against minor shoulder discomfort.
Ice or Heat
Depending on the nature of your shoulder pain, applying either ice or heat can provide relief. Ice is particularly beneficial for acute injuries or conditions accompanied by inflammation. It helps reduce swelling and numbs the area. In contrast, heat can help relax tense muscles and increase blood flow, which can be beneficial for chronic muscle or joint pain. Use these modalities as directed and avoid applying ice or heat directly to the skin to prevent injury.
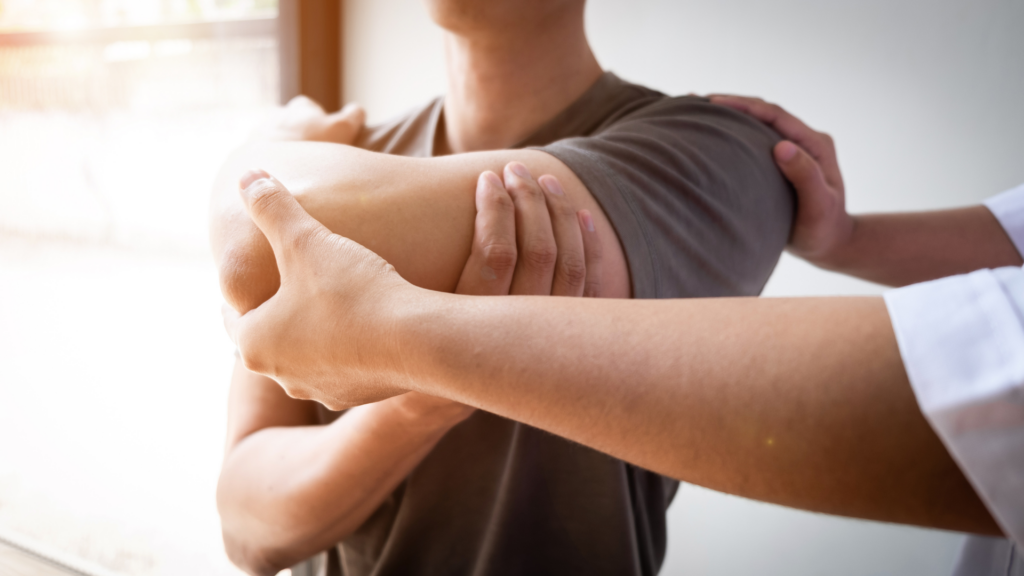
Physical Therapy
When shoulder pain persists or is related to musculoskeletal issues, seeking the guidance of a physical therapist can be highly effective. Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the recovery process, helping you regain mobility and reduce pain.
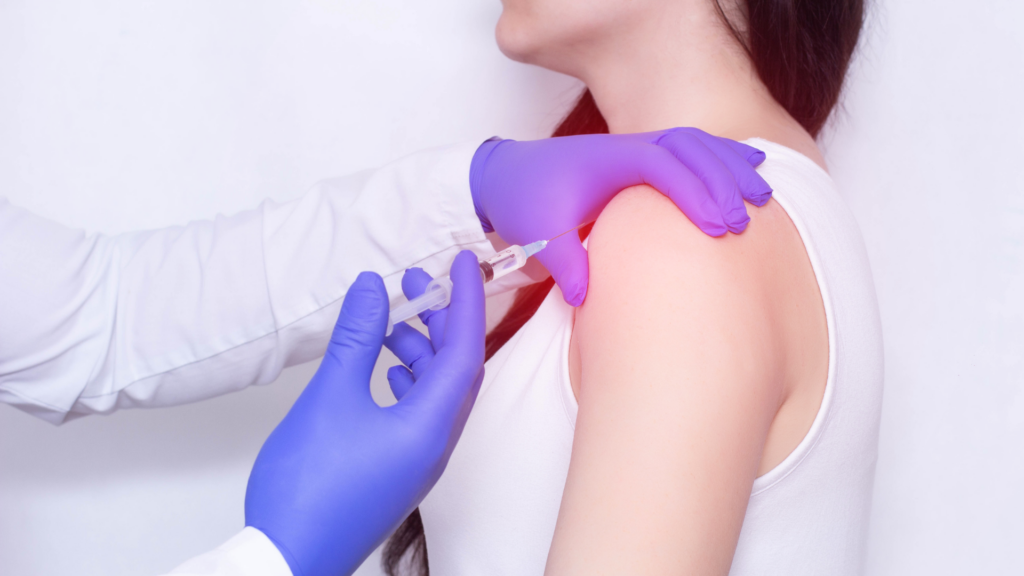
Minimally Invasive Treatments
In cases where shoulder pain is severe or chronic, and more conservative treatments have not provided sufficient relief, there are minimally invasive treatments available. These may include:
Coreflex Injections
Coreflex injections, also known as corticosteroid injections, can be administered directly into the shoulder joint to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. They can be particularly beneficial for conditions like bursitis or tendinitis.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves the injection of a concentrated solution of your own platelets, which contain growth factors, into the affected area. This treatment aims to stimulate tissue repair and reduce pain. PRP therapy is often considered for conditions like rotator cuff injuries or osteoarthritis.
Seeking appropriate medical care and guidance based on the nature and severity of your shoulder pain is essential for effective management and recovery. Our Pain Doctor can diagnose the underlying cause of your pain and recommend the most suitable treatment options to help you regain comfort and function in your shoulder.
If your shoulder pain is severe, persistent, or worsening, or if it is accompanied by concerning symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea, seeking immediate medical attention is paramount. Do not delay in calling 911 or going to the nearest emergency room. Such symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying issue, including a heart attack or other critical medical conditions that require urgent intervention.
Conclusion
Shoulder pain is a symptom that can have various causes, ranging from benign to potentially life-threatening. Recognising when shoulder pain might be a sign of a heart attack is crucial for early intervention and treatment. By understanding the specific characteristics, associated symptoms, and risk factors of cardiac-related shoulder pain, individuals can take prompt action to seek medical help when needed.
It’s essential to be aware of other potential causes of shoulder pain, such as muscle and soft tissue issues, joint and bone-related problems, nerve-related and referred pain, as well as internal health issues. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing shoulder pain effectively and ensuring overall health and well-being. Nevertheless, when shoulder pain occurs, it should not be ignored, and seeking medical advice when in doubt is always the safest course of action. Shoulder pain can be a signal from your body, and responding to it with caution and care can make all the difference in your health and recovery.