Middle back pain, a prevalent health concern affecting individuals of all ages, can significantly impact one’s quality of life and daily functioning. This discomfort, felt in the thoracic spine region, between the upper cervical spine and the lower lumbar spine, demands an extensive understanding of its origins, identification of symptoms, and the implementation of effective treatment strategies.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate details of middle back pain, exploring its anatomical context, diverse causes, recognizable symptoms, and the array of diagnostic and therapeutic approaches available. By shedding light on this prevalent issue, individuals can empower themselves with the knowledge to better comprehend, manage, and seek appropriate medical attention for middle back pain.
What is Middle Back Pain?
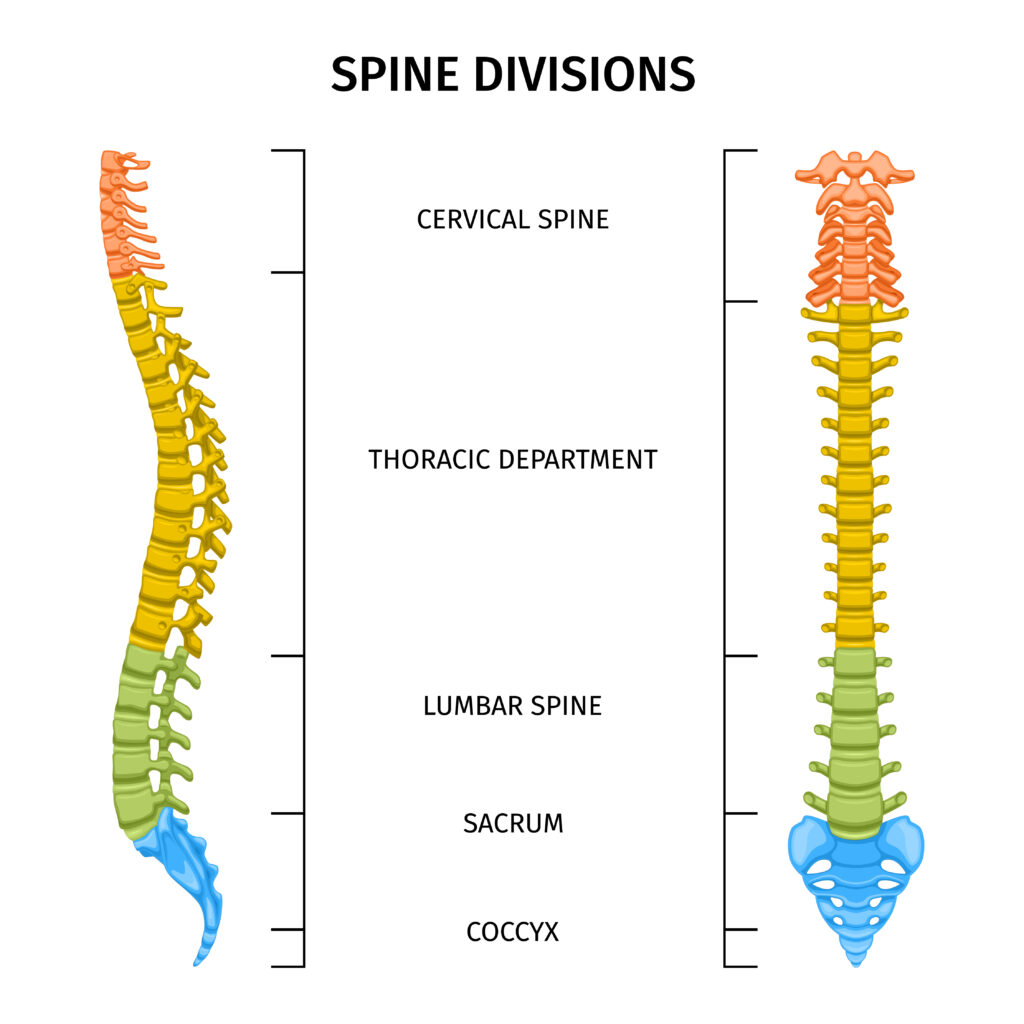
Middle back pain, often referred to as pain in the middle of the back or middle side back pain, is a common ailment that affects individuals across various age groups. This discomfort is characterised by pain or discomfort felt in the thoracic spine region, which is the middle portion of the spine located between the upper cervical spine (neck) and the lower lumbar spine (lower back). Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies are crucial steps in effectively managing middle back pain.
Middle back pain can manifest in various forms, ranging from a persistent, dull ache to sharp, sudden pain. It might be localised to a specific area or radiate to adjacent regions. Due to the complex structure of the thoracic spine and its connections to other parts of the body, middle back pain can sometimes be associated with other health conditions. This makes it imperative to gain a deeper understanding of its anatomical context and the potential sources of discomfort.
Common Causes of Middle Back Pain
When it comes to middle back pain, understanding the underlying causes is essential: as it helps pinpoint the source of discomfort and guides effective treatment strategies. Below are some of the common causes of middle back pain:
Poor Posture
One of the primary contributors to middle back pain is poor posture. Modern lifestyles, characterised by prolonged periods of sitting and hunching over electronic devices, can lead to musculoskeletal imbalances. These imbalances strain the muscles and ligaments in the thoracic region, leading to discomfort. Addressing posture-related middle back pain often involves ergonomic adjustments, mindful body alignment practices, and exercises aimed at strengthening the supporting muscles.
Muscle Strain and Overuse
Muscle strain resulting from overuse, sudden movements, or improper lifting techniques can cause middle back pain. Engaging in activities that the body isn’t accustomed to, or overexerting the muscles without proper warm-up, can lead to microscopic damage in muscle fibers. This damage triggers pain and inflammation. Effective management involves rest, gentle stretching, and gradual reintegration of activities.
Slipped (Herniated) Discs and Spinal Problems
Slipped disc, or herniated disc occurs when the soft gel-like center of an intervertebral disc protrudes and puts pressure on surrounding nerves. This condition can cause sharp, shooting pains in the middle back and sometimes lead to referred pain in the arms or legs. Other spinal issues such as spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal) or degenerative changes in the spine’s structures can also contribute to middle back pain. Treatment options range from physical therapy to surgical interventions, depending on the severity.
Lifestyle Factors: Stress and Obesity
Psychosocial factors like chronic stress can lead to tension in the muscles of the middle back, resulting in discomfort. Additionally, excess body weight places strain on the spine and supporting structures, contributing to pain. Addressing lifestyle factors through stress management techniques, weight loss strategies, and regular exercise can play a significant role in alleviating middle back pain.
Signs and Symptoms of Middle Back Pain
Recognising the signs and symptoms of middle back pain is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action. Differentiating between a dull ache and sharp pain, understanding when the pain worsens or eases, and being aware of associated symptoms such as numbness or tingling can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause of the discomfort.
Dull Ache or Sharp Pain: Recognising the Difference
Dull, persistent aches often indicate muscle-related issues or postural problems, while sharp, sudden pain might be attributed to more acute causes like disc herniation or spinal misalignment. The location of the pain, whether it’s centered in the middle back or radiates to other areas, also provides diagnostic clues.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
Knowing when to consult a medical professional is pivotal in preventing further complications. In severe cases, enduring middle back pain that disrupts daily routines or exhibits accompanying worrisome symptoms such as weakness, numbness, fever, or unexplained weight loss, it is advisable to promptly consult a Pain Doctor. Timely intervention can prevent potential escalation of the issue and aid in identifying and addressing underlying health conditions.
Diagnosing Middle Back Pain
Accurate diagnosis forms the cornerstone of effective middle back pain management. Our Pain Doctors employ a combination of methods to pinpoint the root cause:
Physical Examination and Medical History
Pain Doctors conduct a thorough physical examination to assess posture, range of motion, muscle tenderness, and any visible abnormalities. Additionally, they gather a detailed medical history, including information about lifestyle, occupation, and the timeline of symptom onset. This information is instrumental in facilitating an accurate diagnosis., provides valuable context for diagnosis.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, and CT Scans
Advanced imaging techniques like X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans offer detailed views of the spine’s structures. These tests aid in identifying issues like fractures, disc herniations, and spinal abnormalities. At Singapore Paincare, our team of experienced primary care doctors and pain care specialists, along with orthopedic experts, collaborate to evaluate your condition comprehensively. In certain cases, an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan might be recommended to assess the severity of conditions such as spinal fractures.
By amalgamating the insights gained from thorough examinations and diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can formulate personalized treatment plans that address the specific causes of middle back pain. These plans encompass a range of therapeutic interventions, including conservative approaches like physical therapy, pain management techniques, and, in severe cases, surgical procedures tailored to individual needs.
Treatment Options for Middle Back Pain
Effectively managing middle back pain entails a range of treatment options, each tailored to the specific needs of the individual. From conservative approaches to surgical interventions, understanding the available treatments is crucial for informed decision-making.
Conservative Approaches
Middle Back Pain can significantly disrupt daily activities and diminish one’s quality of life. Fortunately, several conservative treatment approaches offer effective ways to manage and alleviate middle back pain without resorting to surgical interventions.
One of the primary conservative methods for treating middle back pain is physical therapy. A physical therapist can assess the individual’s posture, movement patterns, and muscle imbalances to develop a tailored exercise regimen. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles of the back, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall spinal stability. Additionally, manual therapies such as spinal manipulation, mobilisation, and soft tissue manipulation can be employed by trained professionals to release tension, improve joint mobility, and reduce pain.
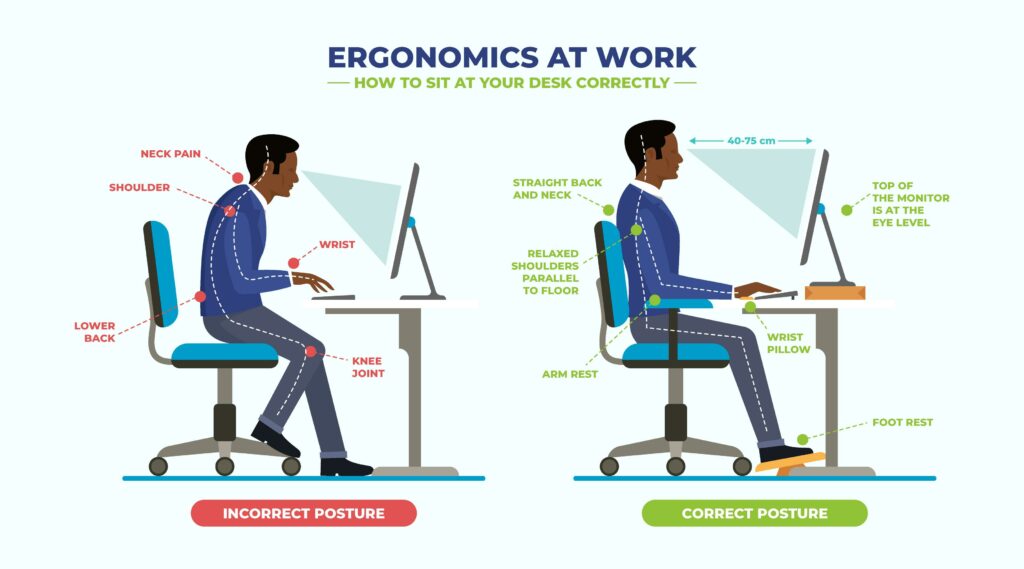
In conjunction with physical therapy, ergonomic adjustments play a crucial role in managing middle back pain. Modifying the workplace environment, chair height, desk setup, and computer screen position can all contribute to maintaining proper posture and reducing strain on the back muscles. Furthermore, lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing stress-reduction techniques like yoga or mindfulness meditation can help prevent the recurrence of middle back pain. By combining these conservative approaches, individuals suffering from middle back pain can often experience significant relief and improve their overall spinal health without the need for more invasive treatments.
Rest and Physical Therapy
In many cases, allowing the affected area to rest and heal is the initial step in treatment. Coupled with this, physical therapy plays a pivotal role. Physiotherapists design personaliszed exercise routines that target muscle imbalances, enhance flexibility, and strengthen the supporting structures of the spine. These exercises not only alleviate pain but also prevent future recurrences.
Medications and Pain Management
For temporary relief, over-the-counter pain medications can be effective. However, it’s important to consult a Pain Doctor before starting any medication regimen. In cases of chronic pain, doctors might prescribe medications that address inflammation and nerve-related discomfort.
If you’re searching for an effective approach to manage your middle back pain caused by a middle back pain, we welcome you to consider our pain management treatments. At Singapore Paincare, our commitment lies in delivering non-invasive solutions that alleviate symptoms while reducing the potential risks, complications, and recovery time typically linked to surgical interventions. Our specialised injections and minimally invasive procedures are designed to target and alleviate the sources of pain in a safer and more gentle manner, specifically tailored to middle back issues.
Minimally Invasive Treatments
Certain minimally invasive treatments can provide targeted relief for middle back pain. Such treatment includes:
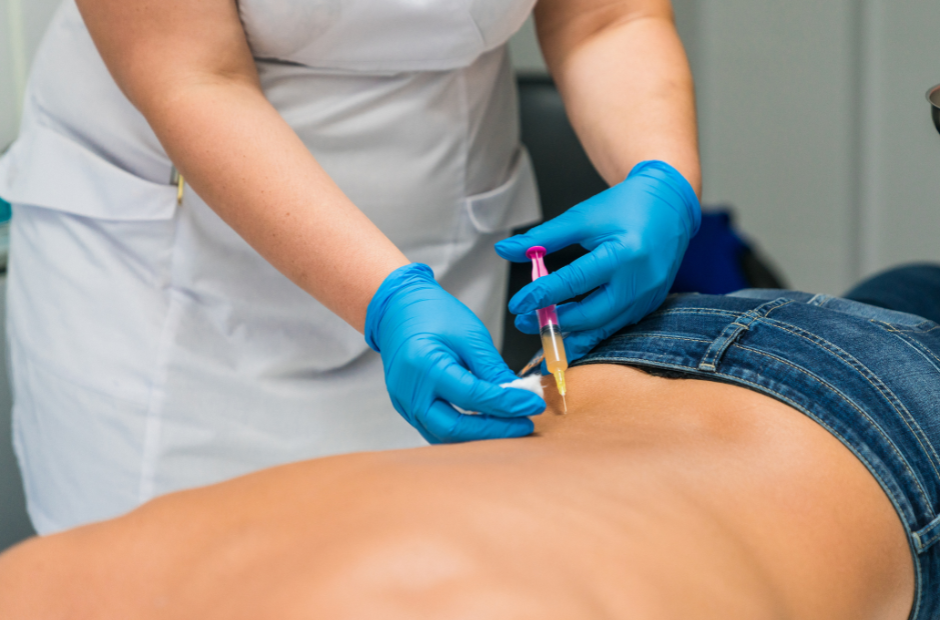
Coreflex injection can addresses middle back pain by targeting the affected tendon, muscle areas, to alleviate muscle spasms, inflammation, and promote healing. This minimally invasive approach delivers profound pain relief to the affected muscles, particularly those associated with trigger points—painful knots in the muscle—and the injured areas.
Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) Therapy involves using a patient’s own blood to extract growth factors to trigger the healing process. It achieves this by inducing a temporary, mild inflammation at the injection site, which in turn elevates the levels of growth factors, thereby fostering tissue repair and growth.. PRP Therapy offers an effective solution for chronic or long-standing injuries by enhancing the initial healing factors and accelerating the healing process.
Posture Correction and Ergonomics
Maintaining proper posture is pivotal in preventing and managing middle back pain. Ensuring that the spine is properly aligned while sitting, standing, and performing activities can significantly reduce strain on the middle back.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy offer non-invasive approaches to pain relief. These therapies focus on promoting relaxation, improving circulation, and addressing muscle tension.
Surgical Interventions
For severe cases of middle back pain that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options range from spinal fusion to discectomy, and they aim to address the underlying cause of the pain while restoring spinal stability.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Taking proactive steps to prevent middle back pain is as important as managing it. Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence and promote overall spine health.
Exercises and Stretches for a Stronger Back
Engaging in exercises and stretches that strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility can provide long-term benefits. Incorporating exercises that focus on the core, such as planks and bridges, helps stabilize the spine and reduce strain.
Ergonomic Tips for a Back-Friendly Workspace
Creating an ergonomic workspace is essential for preventing middle back pain, especially for individuals with desk jobs. Proper chair height, keyboard placement, and monitor positioning can contribute to maintaining a neutral spine posture.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can exacerbate middle back pain. Incorporating stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can have a positive impact on both mental well-being and physical pain.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Middle Back Pain
Empowerment through knowledge and proactive engagement with healthcare professionals is key to managing middle back pain. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring the array of treatment options available, individuals can take control of their well-being and embark on a journey toward pain relief and improved quality of life.