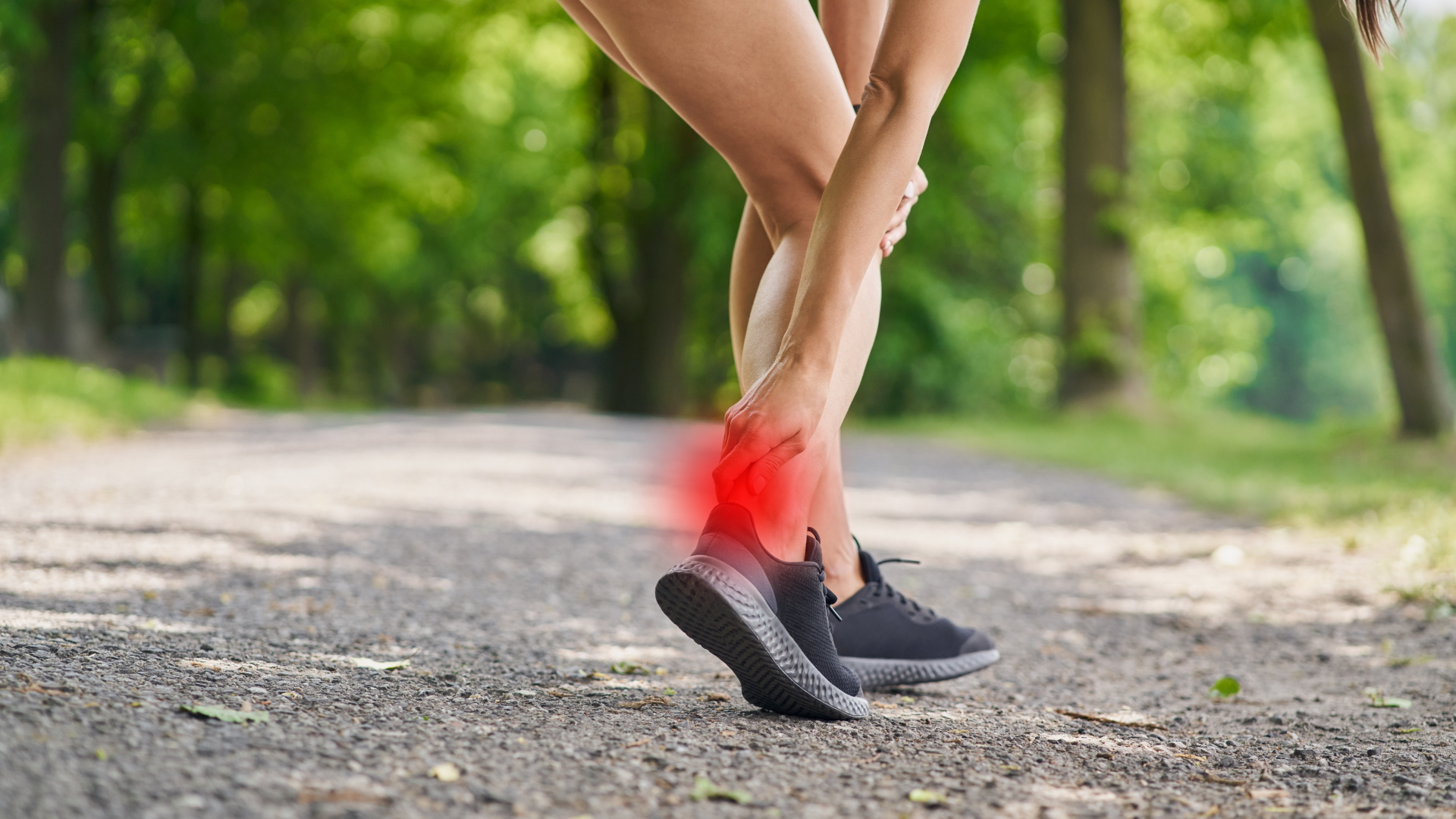
Achilles tendon pain affects many people, especially athletes. This pain can make daily activities difficult and limit your movement and enjoyment in life. To address this issue, it’s important to explore effective treatments and recovery plans. In this article, we’ll look at various ways to manage and heal Achilles tendon pain, helping improve the lives of those who suffer from it.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the anatomy and function of the Achilles tendon is essential for effective rehabilitation.
- Common symptoms of Achilles tendon injuries include pain and stiffness, particularly following periods of inactivity.
- Utilising conservative treatments like physical therapy and the R.I.C.E method can aid in recovery.
- Early intervention often prevents prolonged pain and complications associated with Achilles injuries.
- Identifying risk factors associated with Achilles tendon injuries can help in implementing preventive measures.
- In severe cases, surgical options may be necessary following conservative treatment failures.
- Investing in proper footwear and gradually increasing activity intensity is vital to avoid recurrence.
Understanding Achilles Tendonitis
The Achilles tendon is a strong band of tissue that connects the calf muscles to the heel. It plays a crucial role in how our lower leg functions. This tendon helps us walk, run, and jump by providing both strength and flexibility. When there are problems with the Achilles tendon, it can lead to pain known as Achilles tendonitis. This condition can significantly impact daily activities and sports performance.
What is the Achilles Tendon?
The Achilles tendon is the largest and strongest tendon in the body. It is made up of collagen fibers, which give it strength and support. This tendon is essential for moving the foot, making it vital for walking and running. Keeping the Achilles tendon healthy is important for staying active, especially for athletes and those who engage in regular exercise.
Common Causes of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is primarily caused by overuse, often resulting from repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon during physical activities. Common activities that contribute to this condition include running, particularly on hard surfaces, and participating in high-impact sports like basketball and soccer. Sudden increases in activity level or changes in exercise routine, such as running on hilly terrain, can place additional strain on the tendon. These repetitive motions lead to microtears in the tendon, resulting in inflammation and pain.
Other factors that increase the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis include age, as older adults are more prone to this condition due to decreased tendon elasticity and potential bone spurs that irritate the tendon. Gender also plays a role, with men being at a higher risk. Additional contributors include certain medical conditions, such as psoriasis or high blood pressure, and medications like fluoroquinolones. Obesity can exacerbate the strain on the tendon, while structural issues like flat feet may also increase susceptibility. Recognising these common causes is essential for preventing Achilles tendonitis and maintaining optimal foot and ankle health.
Recognising the Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
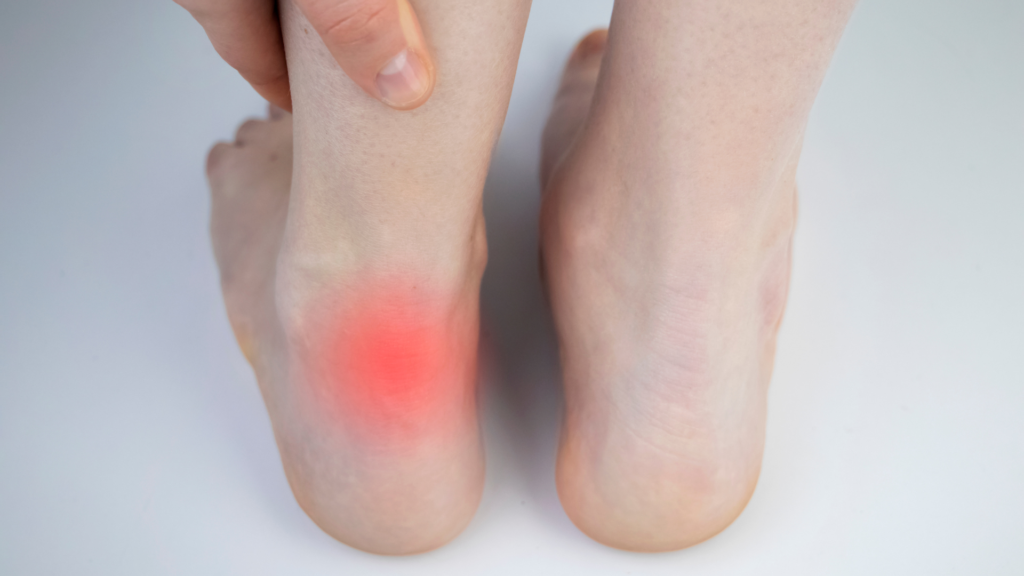
Achilles tendonitis symptoms typically include pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, particularly near the heel, which may worsen with activity and improve with rest. Swelling and tenderness can occur, especially after exercise, and you might experience a noticeable thickening of the tendon. Many individuals report a limited range of motion, making it challenging to walk or engage in physical activities. In some cases, a creaking or crackling sound may be felt during movement. Recognising these symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further injury. If you experience any of these signs, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Impact on Movement and Joint Function
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel, playing a key role in our movement. When it’s injured, our walking mechanics change, leading to heel pain and limited ankle mobility, which can also affect the knee due to added stress from compensatory movements. This can result in discomfort in the knee, hips, or back, as we instinctively adjust our gait to avoid pain. Such altered walking patterns create a cycle of discomfort, highlighting the importance of treating the whole body rather than just the injured area. Addressing these interconnected issues is essential for effective recovery and overall leg health.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, please consider seeking a medical evaluation:
- Persistent pain or tenderness in the back of the heel
- Swelling or inflammation around the Achilles tendon
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of rest
- Difficulty walking, running, or jumping
- A sudden sharp pain during physical activity
- Any signs of infection including fever, redness or warmth at the back of your heel
Seeking professional help early can prevent further injury, speed up recovery, and reduce pain. It also improves mobility and helps avoid chronic conditions. If you’re experiencing symptoms like persistent heel pain or difficulty moving, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider.
Effective Treatment Options for Healing Achilles Tendonitis
Treatment options for achilles tendonitis vary depending on the severity of the injury. Initial approaches typically focus on conservative methods, including rest, ice application, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility, which can aid in the healing process. Gradually returning to activity with proper footwear can also help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense for managing Achilles tendonitis. Resting the affected foot and avoiding activities that aggravate the tendon are essential steps. Ice therapy can reduce swelling and pain, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide additional relief. Engaging in physical therapy focused on stretching and strengthening exercises can help restore function and prevent future injuries. Orthotic inserts or heel lifts may also be beneficial in alleviating stress on the tendon.
Minimally Invasive Treatments for Healing Achilles Tendonitis
For individuals who do not respond to conservative treatments, minimally invasive options may be considered. These techniques aim to promote healing while reducing recovery time. These approaches can be effective in managing symptoms and facilitating a return to normal activity.
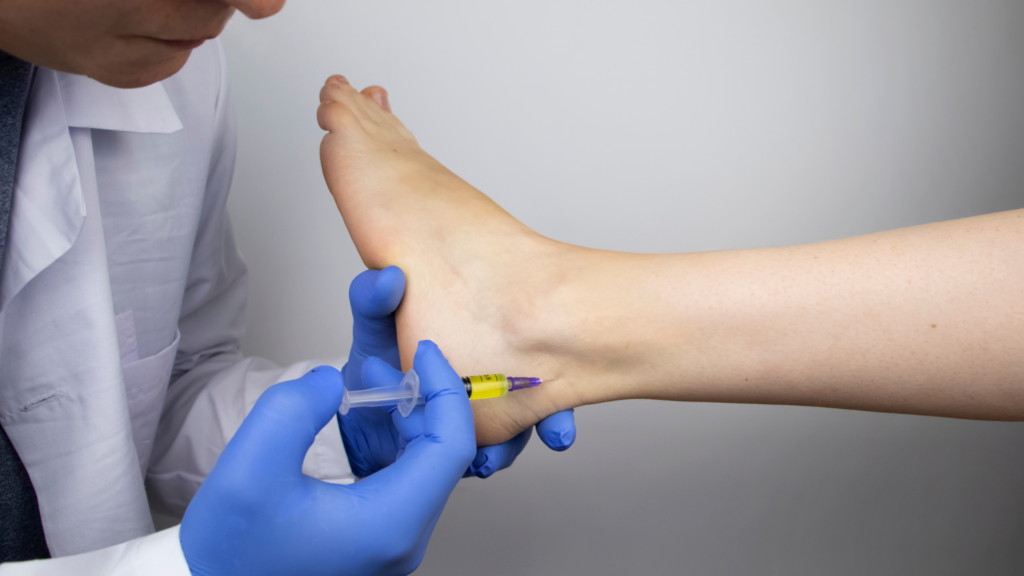
Coreflex Injections
Coreflex injections involve injecting a mixture of medications, including local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory agents, directly into the affected tendon The targeted approach helps reduce swelling and discomfort, allowing for improved mobility and function. Coreflex injections can be particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing chronic pain, as they provide quick relief and can support the healing process.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is another option for treating Achilles tendonitis. This treatment involves drawing a small sample of the patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting this platelet-rich plasma into the injured tendon. PRP contains growth factors that promote healing and tissue regeneration. By enhancing the body’s natural healing processes, PRP therapy can help reduce pain, improve function, and accelerate recovery times. Many patients report significant improvements in symptoms after undergoing PRP therapy, making it a valuable option for those struggling with Achilles tendonitis.
Prevention Tips
Preventing Achilles tendonitis involves proactive measures to maintain tendon health. Warm-up exercises that focus on stretching the calf muscles can help prepare the tendon for activity. It’s crucial to gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activity to avoid overloading the tendon. Wearing appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning can also minimize stress on the Achilles tendon. Incorporating cross-training and varying workouts can help reduce repetitive strain and lower the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Taking a proactive approach to Achilles tendon health can enhance quality of life, allowing individuals to return to their favorite activities and maintain long-term mobility. Treatments like conservative methods, Coreflex injections, and PRP therapy, combined with preventive measures, such as supportive footwear and proper warm-ups, can help minimise the risk of re-injury and support an active lifestyle. If you experience persistent pain or discomfort, don’t wait—see a professional for a proper check-up. With the right care, you can overcome Achilles tendonitis and enjoy a pain-free lifestyle.