Achilles tendonitis is a common injury that can hinder daily activities and sports performance. To cure Achilles tendonitis quickly, it’s essential to adopt a multi-faceted approach that includes immediate rest, ice application, and anti-inflammatory medications. These initial steps can help reduce pain and swelling, allowing for a more effective recovery process. Additionally, exploring minimally invasive treatments like Coreflex injections and PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy can significantly accelerate healing. These therapies target inflammation directly, enhancing the body’s natural healing processes and providing faster relief.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the causes and symptoms of Achilles tendonitis to promote early diagnosis.
- Utilise both conservative treatments and advanced therapies for optimal recovery.
- Seek professional help if symptoms persist or worsen to prevent permanent damage.
- Adopt preventive measures, including proper footwear and gradual training increases.
Understanding Achilles Tendonitis
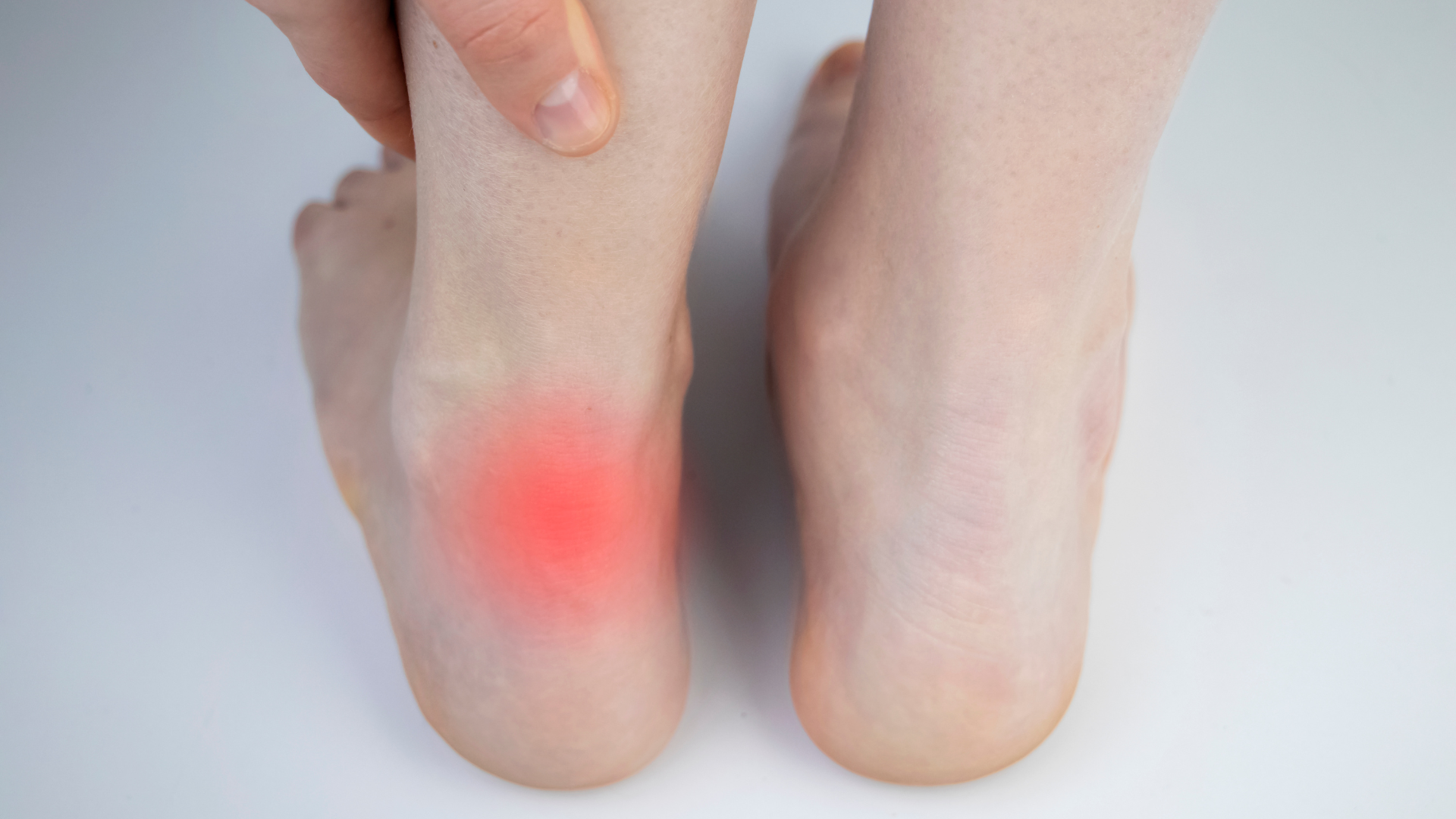
Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition often arises from excessive strain during physical activities, making it vital for athletes and active individuals to be aware of its implications. Understanding the anatomy and function of the Achilles tendon helps in recognising potential injury risks and effective recovery methods.
Causes of Achilles Tendon Injuries
Achilles tendon injuries can occur due to various factors, primarily related to overuse and repetitive stress. Common causes include sudden increases in physical activity, running on hard surfaces, and participating in high-impact sports. Additionally, risk factors such as age, certain medical conditions, and improper footwear can contribute to the likelihood of developing tendonitis, emphasising the importance of understanding these causes for effective prevention and treatment.
Symptoms to Watch for
Recognising the symptoms of Achilles tendonitis is crucial for timely intervention. Common signs include pain and stiffness along the tendon, particularly near the heel, which often worsens with activity. Other symptoms may include swelling, tenderness, and a noticeable thickening of the tendon. Being aware of these indicators can help individuals seek appropriate care before the condition worsens.
Diagnosing Achilles Tendonitis
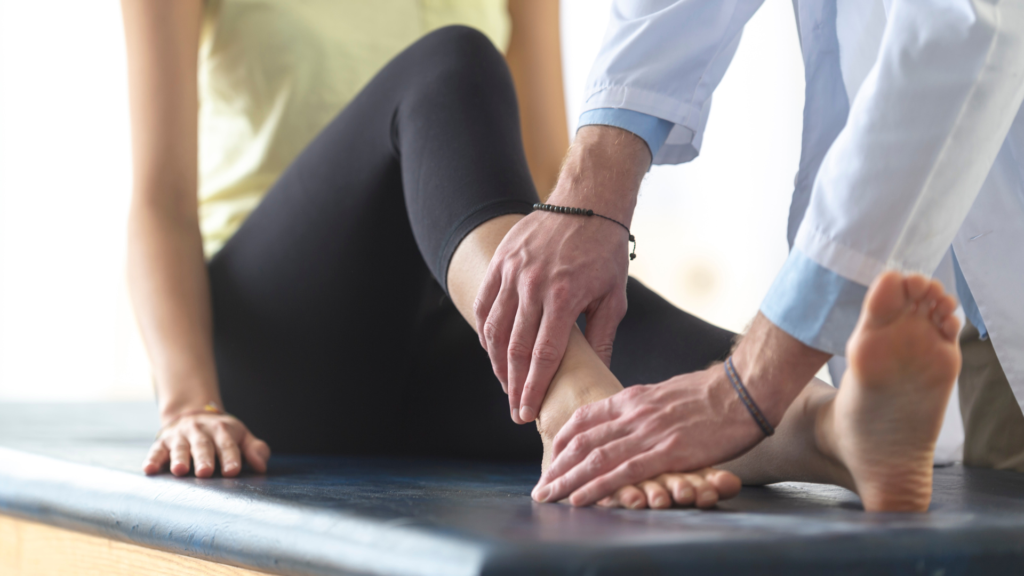
Diagnosing Achilles tendinitis involves a comprehensive approach that begins with a review of your medical history and symptoms, including pain location, intensity, and any activities that worsen the discomfort. A thorough physical examination follows, during which your healthcare provider will assess tenderness, swelling, and range of motion in the ankle and foot. To confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the condition, imaging tests may be recommended, such as X-rays to rule out fractures, MRIs for detailed images of soft tissues, or ultrasounds to assess tendon structure and blood flow.
When to Seek Professional Help
You should seek professional help for Achilles tendinitis if you experience persistent pain in the back of your heel lasting more than three months. This prolonged discomfort, particularly if it interferes with your daily activities or athletic performance, requires a medical evaluation. Additionally, consult a healthcare provider if you notice swelling, stiffness, or difficulty walking, especially after periods of rest. If conservative treatments—such as rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers—have not provided relief, or if you experience sudden, severe pain that may indicate a rupture, it is important to seek prompt medical attention. Early intervention is key to preventing further injury and facilitating a more effective recovery.
Importance of timely intervention to prevent worsening of the condition
Waiting too long to treat tendonitis can lead to worse issues like tendon rupture. Getting help soon not only deals with the pain but also prevents future injury. By sticking to a care plan and knowing when to see a doctor, you can keep active safely and avoid further damage.
Minimally Invasive Treatments for Fast Relief
Minimally invasive treatments offer effective options for fast relief from Achilles tendonitis. These therapies are usually recommended for patients who have tried conservative measures without significant improvement.
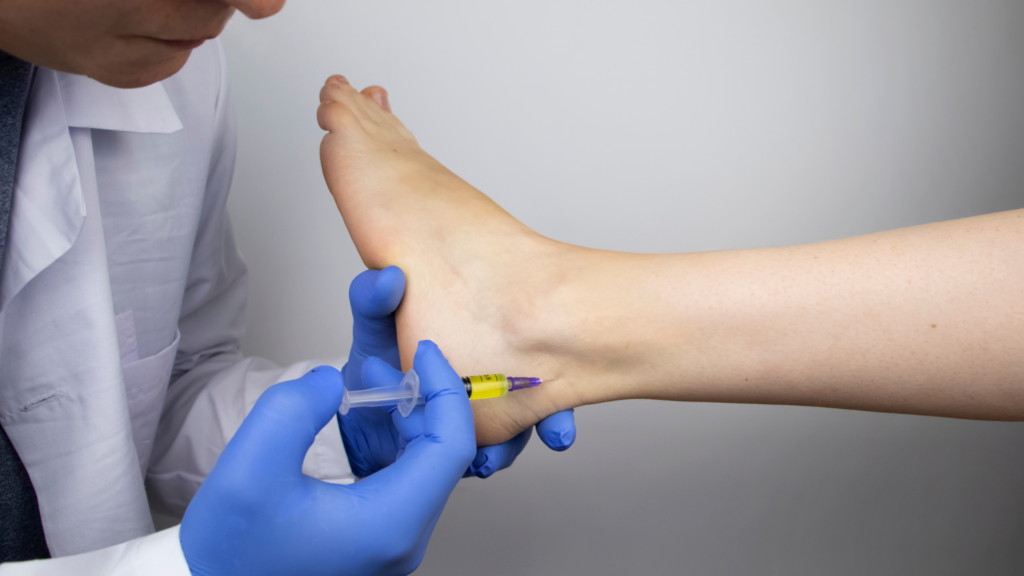
Coreflex Injections
Coreflex injections, which combine local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory agents, provide targeted relief by reducing inflammation directly at the injury site. The precise targeting of the injection helps reduce swelling, allowing individuals to regain mobility more quickly and return to their preferred activities.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a treatment option for Achilles tendinitis that uses the body’s own healing factors to promote recovery. The process involves drawing a small sample of your blood, concentrating the platelets through processing, and injecting this enriched plasma directly into the affected Achilles tendon. This therapy can enhance tissue repair and reduce inflammation due to the high concentration of growth factors in PRP, leading to significant pain relief and improved function after treatment.
Home Remedies
In addition to professional treatments, home remedies can play a significant role in managing Achilles tendonitis. Applying ice to the affected area, using compression bandages, and elevating the foot can help reduce swelling and pain. Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises, when appropriate, can also aid recovery. These self-care measures complement medical treatments and contribute to a holistic approach to healing.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be beneficial for those recovering from Achilles tendonitis, providing tailored exercises to improve flexibility and strength. Early intervention through therapy can aid in preventing future injuries, promoting long-term tendon health.
How to Know It’s Healing
Signs of healing from Achilles tendonitis include a noticeable reduction in pain and swelling, improved mobility, and increased strength in the affected area. Healing times vary based on the severity of the injury: mild cases may resolve within a few weeks, while moderate to severe cases can take several months. Monitoring these indicators can help individuals gauge their recovery progress and make informed decisions about returning to activity.
Prevention Tips
Preventing Achilles tendonitis from recurring requires a proactive approach to tendon health. Key strategies include wearing proper footwear that provides adequate support, performing warm-up exercises to prepare the tendon for activity, and gradually increasing training intensity. By incorporating these measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of re-injury and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Curing Achilles tendonitis quickly requires a comprehensive strategy that incorporates immediate self-care measures, advanced treatments, and preventive practices. By understanding the causes and symptoms of this common injury, individuals can recognise when to seek professional help and avoid long-term damage. Initial conservative treatments such as rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications play a crucial role in managing pain and swelling. For those who do not respond to these measures, minimally invasive options like Coreflex injections and PRP therapy can significantly enhance recovery by targeting inflammation directly. Additionally, adopting preventive strategies, including proper footwear and gradual increases in physical activity, can help maintain tendon health and reduce the risk of recurrence. With timely intervention and a proactive approach, individuals can achieve effective relief and return to their active lifestyles.